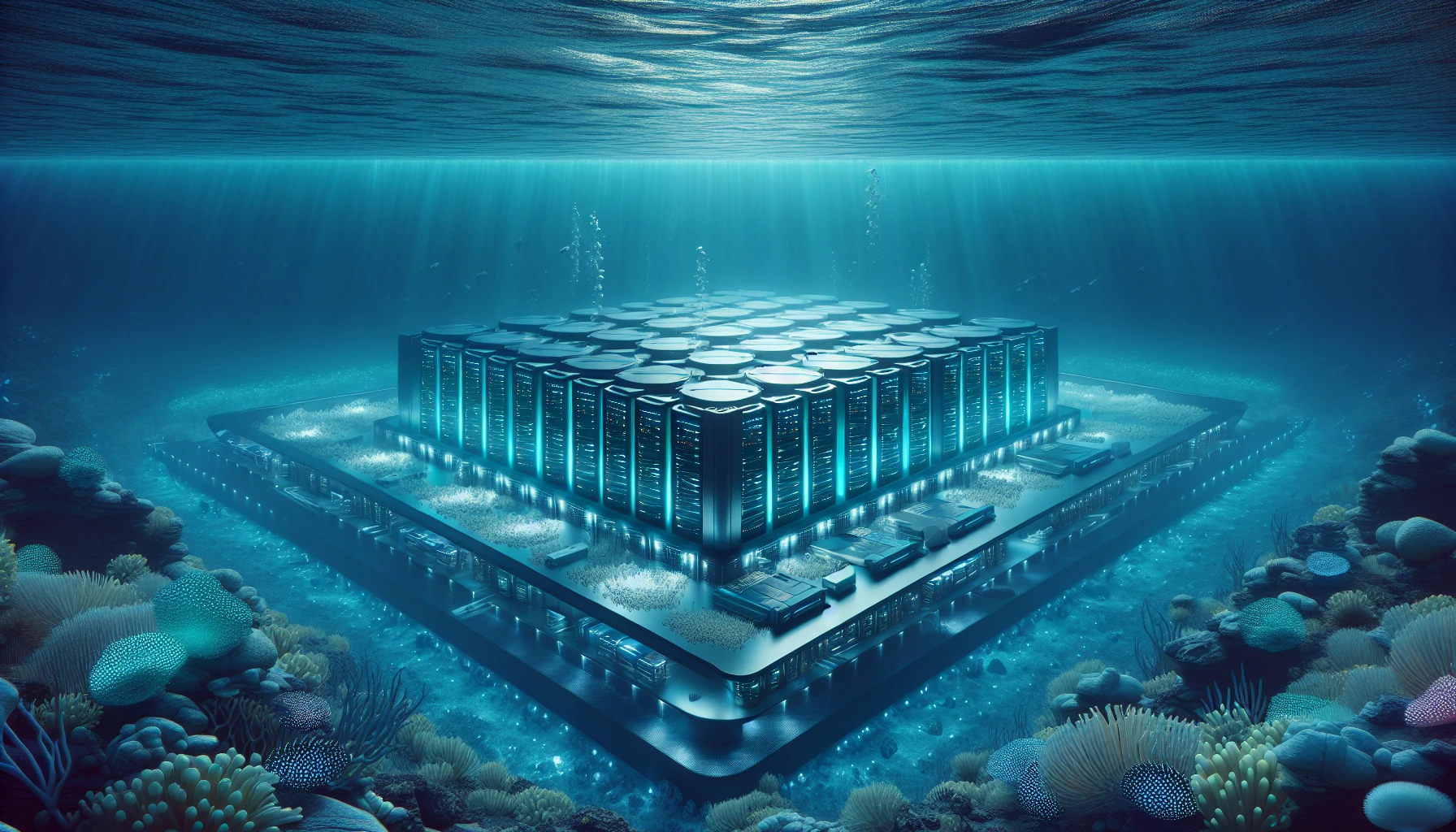
Did you know that there are data centers at the bottom of the ocean? It may sound crazy, but it’s true. While this concept is still experimental, it has the potential to revolutionize waste heat management. In this blog, we will explore the idea of underwater data centers and their advantages. Let’s dive in!
Consistent Cooling and Energy Efficiency
One of the primary advantages of sinking servers underwater is the consistent and relatively cheap cooling it provides. Unlike the surface temperature that varies throughout the day, the bottom of the ocean maintains an extremely consistent cold temperature. This is due to the stratification of deep bodies of water, where colder, denser layers of water remain undisturbed below the heated surface layers.
By surrounding the servers with this consistent low-temperature water, the need for additional energy for cooling is significantly reduced. This not only improves cost and efficiency but also has a positive environmental impact.
Location and Space
Traditional large data centers located in urban areas often face high rent costs as they compete for space with offices, industries, and other businesses. However, underwater data centers offer a unique solution to this problem. By relocating the servers to the bottom of the ocean, they can avoid competing for space and instead coexist with marine life.
If these underwater servers are left untouched for around a decade, the impact on the benthic biome (the ecosystem at the ocean floor) would be minimal. This makes underwater data centers an environmentally friendly option.
Enhanced Server Longevity
Underwater data centers take advantage of sealed environments, similar to those used on land. The servers are placed in airtight containers filled with a dry, neutral gas like nitrogen. This oxygen-free and non-flammable atmosphere prevents corrosion and increases server longevity.
Moreover, the lack of onsite maintenance reduces the risk of accidental damage caused by human-machine interactions. With a significantly lower failure rate, servers can be left in place for extended periods, with drives replaced only during scheduled turnover.
Solving Technical Challenges
While sinking servers underwater presents technical challenges, they are solvable with current technology. Anti-corrosion coatings, such as specialized paint and galvanic protection, can protect submerged metal components. Thick metal walls of cylindrical storage containers can withstand the pressure of seawater at several hundred feet below the surface.
Reliable anchoring systems must also be in place to prevent the shifting of the data centers. Additionally, cables connected to the containers should be wrapped in protective materials and buried below the seabed to safeguard them from animal interference, such as shark attacks.
Conclusion
The idea of underwater data centers may still be experimental, but it offers incredible potential benefits. From consistent cooling and energy efficiency to increased server longevity and minimal environmental impact, this concept could revolutionize the way we manage waste heat and data storage.
While there are some challenges to overcome, current technology and solutions can address them effectively. The future of data centers may lie beneath the ocean’s surface, providing reliable and sustainable solutions for our growing needs.